Unit 1: IBM Maximo asset management overview
Lesson 1: Asset management
• IBM Maximo Asset Management solution
• Asset life cycle management and Maximo
Lesson 2: Framework overview
• IBM Maximo Asset Management
• Architecture
• Connectivity
• Applications and functional areas
• Applications and the User Interface (UI)
• The Start Center
• General interface components
• Asynchronous validation of heads-down data entry
• Asynchronous validation features
• Asynchronous validation benefits
• Data querying and retrieval
• List tab
• Partial word or character string
• Search operators
Lesson 3: Business requirements overview
• Determining requirements
• Flows of business processes
• Business processes that are supported
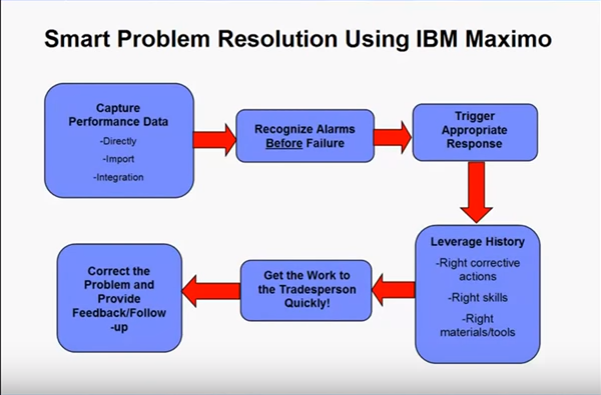
Lesson 4: Performance metrics
• Key performance indicators (KPIs)
• Benchmarks and performance goals
• Maximo key performance Indicators (KPIs) and reports
• KPI Manager application
• Start Center KPIs
• KPI Cron Tasks
• Report Administration application
• KPIs, reports, and implementation
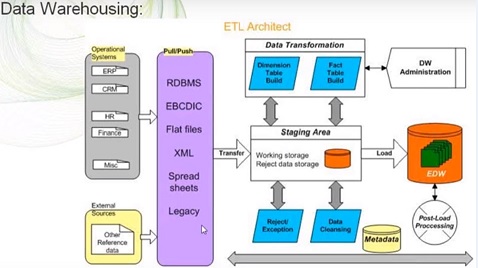
Unit 2: Data setup and configuration
Lesson 1: System configuration and data setup overview
• Initial database setup
• Creating and registering an initial user
• Secondary data and database setup
• Record identification and auto number
Lesson 2: Entering and configuring organizations and sites
• Overview of multisite and multi organization strategy
• Data levels of a multisite and multi-organization environment
• Data that is stored at the system level
• Data that is stored at the set level
• Set types
• Set level setup
• Data that is stored at the organization level
• Data that is stored at the site level
• System, set, organization, and site interrelationships
• Graphical overview of interrelationships
• Planning organizations and sites
• Example 1: Multiple locales as one site
• Example 2: Multiple locales as separate organizations
• Record identification and numbering considerations
• Organizations and site setup
• Creating and activating organizations and sites
• Organizations application: Addresses tab
• Organizations application: Sites tab
• Data pre requisites for organization setup
• Currencies and organizations setup
• GL accounts and organizations setup
• GL accounts and organizations
• Account components
• Account code
• GL order and component sequence
• GL Order field
• Required check box
• Chart of Accounts
• Minimum requirements
• Defining the GL component code
• Sets and organizations setup
• Sets and organizations setup rules
• The Sets application
• Automatically creating companies
• Deleting and deactivating organizations and sites
• Deleting an organization
• Deactivating an organization
• Activating an organization
• Deactivating a site within an organization
• Organizations Select Action menu
• System-level options
• Autonumber seeds
• Autonumber prefixes
• Set-level options
• Organization-level options
• Organization-level option considerations
• Organization-level option descriptions
• Site-level options
• Site-level option considerations
• Site-level option descriptions
Lesson 3: Defining and organizing the classifications hierarchy
• Classifications overview
• Classifications use case
• Classifications and attributes overview
• Classifications and attributes use case
• Classifications setup
• Working with attributes and domains
• Setup considerations
Lesson 4: Defining and creating locations and location hierarchies
• Locations overview
• Additional points
• Location hierarchy.
• Parent-child design
• Location example
• Systems overview
• Location types
• Location status
• GL accounts to use and considerations
• Priority use and considerations
• Priority ranges
• Failure Class field
• Locations and systems setup
• System setup process
• Setup questions to consider.
• Setup tips
Lesson 5: Defining and registering users and labor
• Everyone is a person
• Person records.
• Status
• The Person Groups application
• Security groups and user profiles
• The security module
• Implementation questions to consider
• The Security Groups application
• The Users application
• Managing users
• Security groups and user profile setup
• Dependent versus independent groups
• Conditional access and data restrictions
• Data and attribute restrictions
• Conditional option access
• Implementation security groups
• LDAP, SSO, PKI, and PKE
• Labor and craft records
• Labor setup
• Organization labor options
• Multiple skill levels for crafts
• Crafts setup
• Inheritance pay codes
• Setup questions to consider
• Craft and labor key performance indicators
Unit 3: Item and asset planning and setup
Lesson 1: Item and asset setup overview
• Key applications
• Nonrotating versus rotating item
• Review of item sets
• Lesson 2: Defining and setting up items and assets
• Item Master records
• Item Master application
• Storeroom and Inventory management
• Item Master application tabs
• Item tab
• Storeroom tab
• Vendors tab
• Specification tab
• Item Assembly Structure tab
• Inventory application .
• Inventory item reservations
• Specifications and attributes .
• Item Assembly Structure (IAS)
• Nonrotating items setup
• Inventory application tabs
• Inventory tab
• Reorder Details tab
• Rotating Assets tab
• Where Used tab
• Organizations inventory options
• Inventory Defaults options
• ABC Breakpoints
• Reorder option
• Inventory Costs option
Lesson 3: Entering assets information
• Asset setup
• The Asset Templates application
• The Assets application
• Assets Application tabs
• Asset tab
• Maintaining hierarchy and bundling assets
• Failure Class
• Failure Class and Code setup
• Spare Parts tab
• Safety tab
• Meters tab
• Meter setup
• Meter group setup
• Specifications tab
• Asset status
• GL accounts use and considerations
• Priority use and considerations
• Related modules and applications
• Associating people to assets and locations
• Organizations Asset options
Unit 4: Purchasing
Lesson 1: Procurement process and setup overview
• Basic Maximo purchasing process
• Purchasing life cycle and applications
• Supporting data of companies and company master
• Company creation and setup
• Vendors
• Company branches
• Sets considerations .
• Company Master application
• Revisiting the Sets application
• Company Master application considerations
• Company Master application benefits
• Master contracts
• Warranty contracts
• Warranty Contracts application tabs
• Contract tab
• Properties tab .
• Contract Lines tab
• Associated Assets tab
• Terms and Conditions tab
• Warranty Contracts application: Select Action menu
Lesson 2: Requisitioning
• Requisitioning overview
• Purchase Request (PR) types
• Purchase requests
• Desktop Requisitions
• Request for quotations
• PR status
• PR lines
Lesson 3: Purchase Orders (POs)
• Purchase order
• Purchase ordering overview
• Methods for creating POs
• PO status
• Waiting on approval and approval limits
• Editing POs
• Approving POs
• Revising POs
• Canceling POs
Lesson 4: Receiving materials and services
• Receiving materials and services
• Receipt types
• Completion of receipts
• Line status
• Holding locations
• Statuses
• Lesson 5: Invoice reconciliation
• Invoices overview
• Key terms
• Types of invoices
• Invoice statuses
• 3-1 match
• Basic process for invoice reconciliation
Unit 5: Work management
Lesson 1: Work management processes and setup overview
• Work occurrences
• The Work Orders module
• Work Orders module applications
• Additional modules and applications that support work orders
• Module Relationships diagram
• Work orders and assets
• Work orders and inventory
• Work orders and purchasing
• Work orders and planning
• Work orders and preventive maintenance
• Work orders and service requests .
• Work order life cycle
• Organizations work order options
• Managing work orders
• Work types
• Work order status
• Work order priority
• Priority value range Implementation Considerations
• Instructor demonstration
Lesson 2: Setting up job plans
• Job plans
• Work plans
• The Planning module
• Setting up job plans
• Job Plans application
• Job Plans application tabs
• Job Plan subtabs
• Organization and site fields
• Job Plans, organizations, and sites
• Labor
• Materials
• Applying the job plan to work orders
• Meters and tasks
• Job Plan Tasks window
• Job plan overview
• Task numbering and sequencing
• Subtabs
• The Labor subtab
• The Materials subtab
• The Services sub tab
• The Tools subtab
• Adding work assets to a job plan
• The Work Assets tab
• Job Plan status
Lesson 3: Setting up scheduled or routine work
• PM KPIs
• Preventive maintenance (PM) options
• Setting up PMs
• Preventive Maintenance (PM)
• Work assets and PMs
• Preventive Maintenance application tabs .
• Important fields on the PM tab
• PM frequencies
• The Frequency tab: Work order generation information
• Fixed and floating PM schedules
• The Seasonal Dates tab
• The Job Plan Sequence tab
• How Maximo selects a sequenced job plan
• The PM Hierarchy tab
• PM generation
• Time-based PMs
• Meter-based PMs
• Important meter-based PM fields
• Last work order information section
• Next Work Order projections section
• PM status
• Master PMs
• The Master PM application
• Associated PMs
• Considerations in creating and associating Master PMs
• Master PM tabs
Lesson 4: Creating and generating tickets and work orders
• Applications working together
• Work Order (WO) creation
• Generating PM work orders
• PM Work Order generation methods
• Generating a work order from an asset meter reading
• Generating a work order record with Quick Reporting
• Service desk tickets
• Applying routes to a work order
Lesson 5: Planning work
• Applications working together
• Work plans
• Planning by using Work Order Tracking
• The Plans tab
• The Log tab
• Material reservations
• Viewing material availability and reservations
• Modifying work order work plans
• Children inheriting a parent status change
• Creating a job plan from a work plan
• Removing work plans
• Children WO status
Lesson 6: Assigning work
• Applications working together
• Work assignments
• Assignments
• The Assignment Manager application
• Considerations: Organizations, sites, and calendars
• Work Orders and a work group
• Work list status definitions
• Assigning work to a laborer
• Viewing work assignments
• Dispatch function overview
• The Start Assignment action
• The Interrupt Assignment action
• The Finish Assignment action
• Interrupting an assignment
• Restarting an interrupted assignment
Lesson 7: Initiating work
• Applications working together
• The Inventory Usage application
• Initiating work
Lesson 8: Completing and reporting on work
• Applications working together
• Actuals reporting applications .
• Accepting charges .
• COMP and CLOSE statuses
• COMP status and actual finish time
• Indicating a COMP status on the work order
• Indicating a CLOSE status